Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming technique that revolves around the concept of "objects". Objects are nothing but real-world entities around us like students, birds, mountains, chairs, etc. By utilizing OOP, developers can create applications at a higher level, where the focus shifts from controlling the flow of execution to objects interacting with one another in predefined ways. This approach grants programmers the ability to create new programs or systems by combining software objects. This article is a continuation of the learning Java series.
Table of Contents : Object Oriented Programming (OOP)
- Object in OOP
- Classes in OOP
- Four pillars of object oriented programming
- OOP in Java
- MCQs on OOP
- Short Question on OOP
In the real world, objects are
ubiquitous and can be classified into various categories. For instance, humans,
vehicles, libraries, rivers, watches, and fans are examples of physical
objects, while logical objects include examination results and bank
accounts. Each real-world object possesses distinct characteristics and behaviors.
For instance, humans have characteristics such as gender, age, height, weight,
and complexion, while their behaviors encompass walking, eating, working,
reacting, and more.
The Object Oriented philosophy suggests that the things manipulated by the program should correspond to things in the real world.
- Classification is called a Class in OOP
- Real-world entity is called an Object in OOP
- Characteristic is called Property in OOP
- Behavior is called a Method in OOP
Class in OOP
A class is the
building block in Object-Oriented Programming. It can be defined in multiple
ways:
- A class is a blueprint for an object.
- A class is a user-defined data type.
- A class is a collection of objects of the same kind.
- A class is a user-defined data type that combines data and methods.
A class describes both the data and behaviors
of objects. It contains data members (also known as field or property or
data) and member functions (also known as method or action or behavior). An object is an instance of a class and can be
thought of as a variable that belongs to a specific class. It serves as a data
structure that combines both data and functions within a single entity. Objects
in object-oriented programming (OOP) are akin to real-world entities,
representing the basic runtime entities in the program.
The following figure shows some common real-world classes with their
properties and behaviors.
Object in OOP
In the Java programming language, class variables are commonly referred to as objects. By utilizing objects, we can access the member variables and member functions defined within a class. Objects represent various entities such as people, places, or items that a program interacts with.
For instance, if we have a
class called "Country," the objects of that class can include
Pakistan, China, Japan, the United States, and so on. A single class can create
any number of objects as shown in the following figure.
Figure: Creating objects from a class
Following table shows some real-world class and their objects. Note that you can create as
many objects of a class a many you want. But every object will have its own set
of attributes and functionalities.
Some classes and their objects
|
Class |
Objects |
|
Person |
Allen Turing, Elon Musk,
Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan |
|
University |
Islamia University of
Bahawalpur, Punjab University, Comsats University |
|
Book |
Quran Majeed, C++ in hand,
Let us C, Rich Dad Poor Dad |
|
Student |
Aqsa, Ali, Chris, Nadeem,
Shakeel, Usman Ch. |
|
Cold Drinks |
Coca Cola, Pepsi, Marinda,
Gourmet Cola, Next Cola |
|
Social Media |
Facebook, Twitter,
Instagram, LinkedIn |
|
Fee |
Tuition Fee, Examination
Fee, Check-up Fee |
Class vs Object
The following table shows the difference between class and object.
|
Class |
Object |
|
1. For a single class there can be any
number of objects. For example - If we define the class as River then Sutluj,
Ravi, and Sindh can be the objects of the class River. |
There are many objects that can be
created from one class. These objects make use of the methods and attributes
defined by the belonging class. |
|
2. The scope of the class is
persistent throughout the program. |
The objects can be created and
destroyed as per the requirements. |
|
3. The class can not be initialized
with some property values. |
We can assign some property values to
the objects. |
|
4. A class has unique name. |
Various objects having different names
can be created for the same class |
Four Pillars of Object-Oriented Programming
There are four pillars of OOP that provide real power to OOP.
- Abstraction
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Encapsulation
Let us discuss these one by one
Abstraction
Abstraction is a key concept in OOP that involves presenting
only relevant data and hiding unnecessary details from the user. It allows
users to interact with objects without being concerned about the underlying
implementation. For example, when logging into a Facebook account, users enter
their credentials and click "login" without needing to know how the
data is sent to the server or verified. Abstraction simplifies complex
processes, allowing users to focus on essential tasks and improving code
maintainability and user experience.
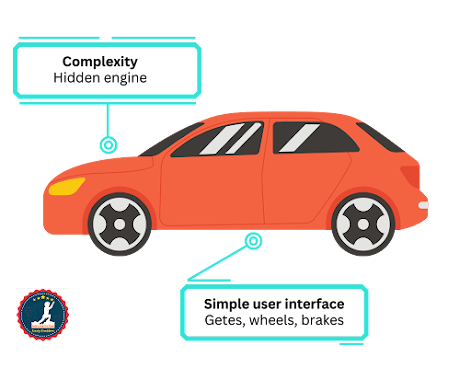
Let's explore another example of abstraction. Consider a car object. It consists of smaller components like the gearing system, steering mechanism, and engine, each of which has its own subsystems. However, for an ordinary person, a car is just a singular object that can be operated effectively through its subsystems. He will not consider about internal subsystems of the car. In this way, abstraction plays a crucial role in simplifying complex real-world systems. In Java programming, abstract classes and interfaces are utilized to achieve abstraction. In Chapter 7, we will delve into a more comprehensive discussion of this concept, providing a deeper understanding of how abstraction is applied in Java and its significance in implementing real-world systems.
Inheritance
Inheritance involves the concept of the parent-child
relationship. In inheritance, the child object gets all the properties and
behaviors of the parent object plus it has also its properties and behaviors.
It provides code reusability. Inheritance is used to achieve runtime
polymorphism. In Java, we extend other classes and implement Interfaces to
achieve inheritance. We will discuss inheritance in detail in the coming articles.
Polymorphism
When one task can be performed in multiple ways i.e. known as polymorphism.
For example, to convince the customer differently, to draw something e.g. shape
or rectangle, etc.
In Java, we use method overloading and method overriding to
achieve polymorphism. Another example can be to speak something e.g. cat speaks
mew, a dog barks woof, etc. Figure showing how the same person behaves
differently in different situations.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation refers to the binding or
wrapping of code and data into a single entity. It is like a capsule that
contains various medications. In the context of Java programming, a class exemplifies
encapsulation. A Java bean serves as a prime example of a fully encapsulated
class. The intricate details of encapsulation will be thoroughly explored in
Chapter 6, providing a comprehensive understanding of this concept.
Object Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java
Java, as both a high-level language and platform, has gained
immense popularity as one of the most widely used object-oriented programming
languages. It offers a secure, robust, and powerful environment for developing
various software applications. In the context of programming, a platform
refers to the hardware or software used to execute programs. Java, with its own
Application Programming Interface (API) and runtime environment (JRE), can be
considered a platform in itself.
According to Sun, approximately 3 billion devices run Java,
highlighting its widespread adoption. It is utilized in developing diverse
applications, ranging from desktop applications such as PDF readers, media
players, and anti-virus software, to web applications powered by the mighty
Java language. Enterprise applications, characterized by their distributed
nature, such as banking systems, also heavily rely on Java for their
development. Additionally, Java finds applications in mobile app development,
embedded systems, gaming, smart cards, and robotics technology.
To illustrate the basics of Java, let's consider a simple
"Hello" program that provides an introductory understanding of the
language. A detailed explanation of this example will be presented on the next
page, offering a step-by-step guide for better comprehension.
class Sample{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello Java");
}
}
MCQs related to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
1.
Which of the following is
not a pillar of Object-Oriented Programming?
a) Inheritance
b) Encapsulation
c) Abstraction
d) Linear programming
Answer: d) Linear programming
2.
Which pillar of OOP focuses
on combining data and methods into a single construct?
a) Inheritance
b) Abstraction
c) Polymorphism
d) Encapsulation
Answer: d) Encapsulation
3.
Which pillar of OOP allows
objects to inherit characteristics from other objects?
a) Encapsulation
b) Polymorphism
c) Abstraction
d) Inheritance
Answer: d) Inheritance
4.
Which pillar of OOP refers
to the ability of objects to take on many forms?
a) Inheritance
b) Polymorphism
c) Abstraction
d) Encapsulation
Answer: b) Polymorphism
5.
Which pillar of OOP focuses
on simplifying complex systems by showing only relevant information?
a) Abstraction
b) Encapsulation
c) Inheritance
d) Polymorphism
Answer: a) Abstraction
6.
Which pillar of OOP ensures
that objects cannot directly access each other's data?
a) Abstraction
b) Polymorphism
c) Encapsulation
d) Inheritance
Answer: c) Encapsulation
7.
Which pillar of OOP allows for
code reusability and modularity?
a) Abstraction
b) Encapsulation
c) Inheritance
d) Polymorphism
Answer: c) Inheritance
8.
Which pillar of OOP is
closely related to the concept of "is-a" relationship?
a) Polymorphism
b) Abstraction
c) Inheritance
d) Encapsulation
Answer: c) Inheritance
9.
Which pillar of OOP emphasizes
the separation of interface and implementation?
a) Encapsulation
b) Polymorphism
c) Inheritance
d) Abstraction
Answer: d) Abstraction
10.
Which pillar of OOP allows
for flexibility and extensibility in code design?
a) Abstraction
b) Encapsulation
c) Polymorphism
d) Inheritance
Answer: c) Polymorphism
11.
Which pillar of OOP
involves the creation of classes based on existing classes?
a) Inheritance
b) Encapsulation
c) Polymorphism
d) Abstraction
Answer: a) Inheritance
12.
Which pillar of OOP
promotes data hiding and information security?
a) Polymorphism
b) Abstraction
c) Encapsulation
d) Inheritance
Answer: c) Encapsulation
13.
Which pillar of OOP allows
for objects to exhibit different behaviors based on their types?
a) Abstraction
b) Encapsulation
c) Inheritance
d) Polymorphism
Answer: d) Polymorphism
14.
Which pillar of OOP focuses
on representing real-world entities and their relationships in code?
a) Polymorphism
b) Abstraction
c) Encapsulation
d) Inheritance
Answer: b) Abstraction
15.
Which pillar of OOP is not
specific to Java and is a general principle in object-oriented programming?
a) Encapsulation
b) Abstraction
c) Inheritance
d) Polymorphism
Answer: b) Abstraction
Short questions related to Object-Oriented
Programming (OOP)
1. Q: What is Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)?
A: OOP is a programming paradigm
that organizes code around objects that contain data and behavior.
2. Q: What are the four pillars of OOP in Java?
A: The four pillars are
encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.
3. Q: What is encapsulation in OOP?
A: Encapsulation is the bundling
of data and methods into a single unit, allowing data hiding and protection.
4. Q: What is inheritance in OOP?
A: Inheritance is a mechanism
where a class inherits properties and behaviors from another class, promoting
code reuse.
5. Q: What is polymorphism in OOP?
A: Polymorphism refers to the
ability of objects to take on multiple forms and behave differently based on
their types or context.
6. Q: What is an abstraction in OOP?
A: Abstraction focuses on
representing essential features of real-world entities while hiding unnecessary
implementation details.
7. Q: How does encapsulation promote data security?
A: Encapsulation restricts direct
access to data, allowing controlled access through methods, and enhancing data
security.
8. Q: What is the purpose of inheritance in OOP?
A: Inheritance allows the creation
of new classes by inheriting properties and behaviors from existing classes,
enabling code reuse and specialization.
9. Q: How does polymorphism enhance code flexibility?
A: Polymorphism allows objects to
be treated as instances of their own class or as instances of their superclass,
providing flexibility in method implementation.
10. Q: How does abstraction simplify complex systems?
A: Abstraction focuses on the essential features of objects while hiding unnecessary implementation details, making it easier to understand and work with complex systems.
In this article, we have discussed in detail about basics of objected oriented programming, particularly from the perspective of Java. Java is one of the famous OOP languages and it supports all the basic concepts of object orientation i.e., classes, objects, abstraction, polymorphism, and inheritance. We have also compared objects with classes and in the last we touched objected oriented programming (OOP) in Java. Hope this article would help you understand the whole concept. Happy learning :).