Steganography is a famous technique in Information security. It is the art of hiding information within other files. These files are known as a cover of plain text, making them indistinguishable from the naked eye. Steganography is essential in enhancing data transmission and storage security. In this detailed article, we'll explore the world of steganography and investigate how it contributes to the protection of confidential information.
1. The History of Steganography
Steganography's roots can be traced back to ancient
civilizations, where secret messages were concealed within wax tablets,
tattooed on messengers' bodies, or even hidden inside fruit. Fast forward to
the digital age, steganography has found its home in the realm of computer
science. With the advent of digital media, such as images, audio, and video
files, concealing information has become more sophisticated and harder to
detect.
2. How Steganography Works
At its core, steganography relies on the concept of the
cover medium. This medium can be an image, an audio file, a video, or any
digital content that appears ordinary. The information to be concealed, often
referred to as the payload, is embedded into this cover medium using
specialized algorithms. The result is a seemingly unaltered cover medium that
houses a hidden data treasure.
3. Types of Steganography Techniques
Various steganography techniques exist, catering to different types of cover media. Let’s discuss different types of steganography:
Image Steganography:
In this technique, data is hidden within the pixel values of an image file. Altering the least significant bits of the pixels allows for minimal visual impact while accommodating the hidden data.
Audio Steganography:
Concealing data within the audio field can be achieved by manipulating certain frequency components or exploiting imperceptible changes in the sound signal.
Video Steganography:
Similar to image steganography, video steganography hides data within video frames, making use of the temporal redundancy of consecutive frames.
Text Steganography:
This technique involves concealing data within the structure
of textual content, such as changing word order, using synonyms, or modifying font characteristics.
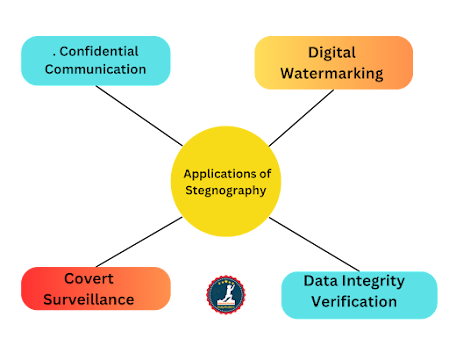
4. Applications of Steganography in Information Security
Steganography serves as an essential tool in various
applications within information security:
a.
Confidential Communication:
Steganography facilitates secure and covert communication
between parties by embedding secret messages within apparent images or audio
files. This is especially useful in scenarios where traditional encryption
might raise doubt.
b.
Digital
Watermarking:
The entertainment industry employs steganography to embed
digital watermarks into media files to prove copyright ownership and prevent
unauthorized distribution.
c.
Covert
Surveillance:
Law enforcement agencies and intelligence organizations
leverage steganography to hide tracking information or covert communication
within publicly available digital content to monitor suspects discreetly.
d.
Data
Integrity Verification:
Steganography can be used to ensure data integrity during
transmission. By embedding checksums or hashes within files, recipients can
verify if the received data is tampered with.
5. Challenges and Countermeasures
Despite its effectiveness, steganography is not without
challenges:
a.
Detection:
Detecting
steganography in cover media can be difficult, requiring specialized tools and
techniques. Steganalysis aims to uncover hidden data, urging steganographers to
continuously refine their methods.
b.
Payload
Capacity:
As the need for increased security arises, striking a
balance between embedding larger payloads and maintaining the cover media's
authenticity becomes a challenge.
c. Security Risks:
While steganography enhances privacy, it can also be
exploited for malicious purposes, like hiding malware or facilitating covert
cyberattacks.
Conclusion
Steganography is a powerful and intriguing technique that
continues to play a significant role in information security. From ancient
civilizations concealing secrets in wax tablets to modern-day digital
steganography revolutionizing data protection, the concept remains as relevant
as ever. By harnessing the power of steganography responsibly, we can ensure
secure communication, protect intellectual property, and safeguard sensitive
information in an increasingly interconnected world.
FAQs : Steganography
1. What is Steganography used for?
Steganography is
used to hide secret data within superficially harmless carrier mediums like
images, audio, video, or text. It serves as a means of covert communication,
digital watermarking, insider threat detection, and secure data transfer.
2. Is steganography hard to detect?
Steganography can be
challenging to detect since the changes made to the carrier medium are often
imperceptible to the human senses. However, with advanced steganalysis
techniques, it is probable to detect and analyze hidden data.
3. What is a real example of steganography?
A real example of
steganography is hiding a text message within the least significant bits of an
image. The image looks unchanged to the naked eye, but the hidden message can
be extracted with the right tools.
4. What are the two types of steganography?
The two types of steganography are digital steganography,
which involves hiding data in digital files, and physical steganography, which
conceals information in the physical world.
5. Which tool is used for steganography?
There are various
tools used for steganography, including OpenStego, Steghide, S-Tools, and
SilentEye, among others.
6. Which tool is mostly used for steganography?
There is no single
tool that is predominantly used for steganography, as different tools offer
varying features and capabilities.
7. What is the basic principle of steganography?
The basic principle
of steganography is to hide information in plain sight by making subtle
modifications to the carrier medium, ensuring that the changes are not easily
detectable.
8. Who invented steganography?
The concept of
steganography dates back to ancient times, making it difficult to attribute its
invention to a specific individual or group.
9. What are the features of steganography?
The features of
steganography include the ability to conceal data, resist detection, and ensure
secure communication between intended recipients.
10. What is the difference between steganography and
cryptography?
Steganography
involves hiding the existence of data, while cryptography focuses on securing
data by converting it into a non-readable format using algorithms and keys.
11. Do hackers use steganography?
Yes, hackers may
use steganography to hide malicious code or sensitive data within seemingly
harmless files to evade detection and perform covert attacks.
12. What is the weakness of steganography?
The weakness of
steganography lies in the possibility of detection through advanced
steganalysis techniques, which can identify hidden information in carrier
mediums.
13. Does steganography use keys?
Yes, steganography
can use keys to encrypt the hidden data, adding an extra layer of security.
14. How safe is steganography?
Steganography can provide
a level of security, but its safety depends on the strength of the encryption
used and the effectiveness of steganalysis countermeasures.
15. How do hackers use steganography?
Hackers use
steganography to conceal malware, exploit code, or steal data within digital
files like images, videos, or documents to bypass security measures.
16. Can steganography be detected?
Yes, steganography can be detected through steganalysis,
which involves using specialized tools and techniques to identify hidden data
within carrier mediums.
17. What is better than steganography?
There is no single
method better than steganography; the choice of security technique depends on
the specific use case and requirements.
18. Where can steganography hide data?
Steganography can
hide data in various digital files, including images, audio, video, and text
documents.
19. Is steganography malware?
Steganography itself
is not malware, but it can be used as a technique to conceal and deliver
malware.
20. Which tool is not used for steganography?
Traditional
encryption tools like AES or RSA are not specifically designed for
steganography.
21. What is the most common form of steganography?
Digital
steganography, where data is hidden within digital files, is the most common
form of steganography in the digital age.
22. What is digital steganography?
Digital
steganography involves hiding data within digital files like images, audio,
video, or text to keep it secret.
23. What crimes are steganography associated with?
Steganography can
be associated with various cybercrimes, including data theft, espionage, and
distribution of malicious software.
24. Is steganography a threat?
While
steganography itself is not inherently a threat, its potential use in
concealing malicious activities makes it a concern for cybersecurity.
25. What is the history of steganography?
Steganography has
a long history, dating back to ancient civilizations, where it was used to hide
secret messages and information.
26. Why use image steganography?
Image
steganography is commonly used because images are ubiquitous, making it easier
to hide data in plain sight without arousing suspicion.
27. Is steganography a type of encryption?
No, steganography
and encryption are distinct techniques. Encryption involves converting data
into a non-readable format using algorithms and keys, whereas steganography
focuses on hiding the existence of data.
28. What was the first example of steganography?
The exact first
example of steganography is challenging to determine due to its ancient
origins, but one early example is the use of invisible ink during medieval
times.
29. Is steganography a science?
Steganography is
both an art and a science, as it involves the creative concealment of data
using scientific methods and techniques.
30. What is forensic steganography?
Forensic
steganography involves the application of steganography to analyze and detect
hidden data in digital evidence for investigative purposes.